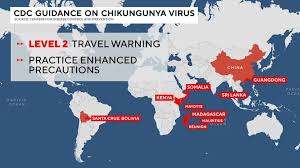
Overview of the Chikungunya Virus Situation
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) has arisen with a stark warning for travelers as cases of chikungunya virus spike abroad. Notably, more than 7,000 infections have been reported in China’s Guangdong province since July, prompting significant health measures in the area. The mosquito-borne virus brings with it severe symptoms like joint pain, fever, and rashes, inciting urgent action among health authorities to safeguard the public.
In hot spots like Foshan, those afflicted are placed in hospitals under mosquito nets, with discharges only permitted after testing negative or after a seven-day isolation period. With the concern over this virus extending beyond China, the UKHSA cautions travelers to adopt protective measures when visiting high-risk regions across Asia, Africa, and South America—areas where the virus is actively transmitted.
Health Recommendations for Travelers
Hilary Kirkbride, Head of Travel Health at the UKHSA, voiced the ongoing risks tied to chikungunya, emphasizing the continuous transmission of the virus globally. Travelers returning to the UK exhibit symptoms, which can lead to heightened alertness at airports and tourist hotspots. Kirkbride advises specific precautions:
- Use insect repellent: Regular applications can dramatically lower the chances of bites.
- Cover exposed skin: Clothing can act as a barrier against mosquito bites.
- Sleep under treated bed nets: Especially in areas with known outbreaks or higher mosquito populations.
Such proactive measures could mean the difference between a tranquil holiday and enduring painful symptoms for weeks or even months thereafter.
Understanding the Chikungunya Virus
Chikungunya, while seldom fatal, manifests significant discomfort. Heat, heightened sensitivity to light, and skin rashes are hallmarks of this affliction. Patients typically see symptom improvement within two weeks, yet many endure lingering joint pain that can last for months or even years.
Experts urge the need for vigilance against mosquito-borne diseases, particularly as global travel increases and more individuals venture into tropical regions. For those planning their next trip or sailing adventure, it becomes crucial to think ahead regarding health advisories and potential risks that could dampen their experience.
The World Health Organization (WHO) underscores the importance of eliminating areas of stagnant water—ideal breeding grounds for mosquitoes. Some progressive measures are already being taken in China, including the use of drones to detect these breeding sites and releasing fish that prey on mosquitoes into local lakes.
Public Reaction and Preparedness Measures
Chinese public response has been mixed, with social media platforms buzzing with comparisons to strict measures seen during the recent pandemic years. Concerns about prolonged effects of chikungunya have been expressed, reflecting a public that is increasingly wary after recent global health crises.
Importantly, it’s crucial to note that chikungunya does not spread from person to person but relies on mosquito vectors for transmission. The virus was first identified in Tanzania in 1952 but has since made its way to over 110 countries, with outbreaks gaining traction due to rising global travel and changes in climate affecting mosquito habitats.
Health authorities in the United States echo similar sentiments, urging travelers to exercise caution, particularly in southern regions of China currently facing outbreaks. Enhanced preventative measures being advised include the use of effective insect repellents and longer clothing during potential exposure times.
Historical Context and Future Implications
Identifying chikungunya’s trajectory sheds light on broader patterns in international tourism. Originally detected over seventy years ago, its spread across various continents poses an ongoing challenge for health systems worldwide, compounded by the ease of global travel. This dynamic underlines why travelers need to remain aware of emerging health threats as they plan their voyages.
Over the years, as travel and tourism have flourished—connecting people through countless destinations—the likelihood of encountering diseases such as chikungunya increases. Infectious diseases often shift landscapes due to climatic changes and heightened urbanization, emphasizing the interconnectedness of global health and tourism.
Travel Preparedness Strategy
Would-be travelers are encouraged to stay informed by consulting health websites and local advisories ahead of their trips. Following guidance from health experts can be pivotal in planning safe adventures, allowing travelers to embrace their journeys with sound strategies and confidence.
In planning beach getaways or yachting adventures, travelers should be vigilant not only about desired destinations but also the health implications associated with those locales. Awareness is key, especially in light of rising health alerts. A few wise steps can ensure enjoyment without the burden of unwelcome ailments.
The global tapestry of travel isn’t merely about reaching new vistas; it encompasses understanding risks that might accompany those journeys. Observations suggest that the tourism landscape will continue to evolve alongside public health dynamics, requiring a balance between adventure and necessary safety measures. For travelers interested in yachting or boating excursions in affected areas, staying abreast of health alerts may prove vital.
Sailing adventures often beckon to stunning marinas and breezy waters, allowing enthusiasts to connect deeply with nature. However, in regions where chikungunya flourishes, precautions should carry equal weight to the thrill of sailing. Always knowing the best practices for staying healthy means the journey can carry on without a hitch.
For those longing to catch the beautiful vistas while navigating the high seas, ゲットボート・ドットコム serves as the go-to choice for an extensive selection of sailing boats and yachts—tapping into the thrill of marine exploration while prioritizing safety during your travels.

 Rising Concerns Over Chikungunya Virus for Travelers">
Rising Concerns Over Chikungunya Virus for Travelers">
